Microbiome from gut to other tissues: the importance of bacterial translocation

How to define microbiota and microbiome?
Microbiome or microbiota? First seen as pathogens, naturally occurring microbes are now recognized as complex and highly diverse assemblages, often associated with a host with whom they interact in a dynamic and beneficial fashion. Microbial communities are commonly defined as the collection of microorganisms living together within a defined environment such as a body part and referred to as the microbiota.
The term microbiome includes the living microbes, their environment but also all the molecules (e.g. nucleic acids, lipids, proteins and metabolites) they and their host produce. Microbiome can also be defined as the collection of genomes and genes from the microbiota members although the term metagenome is preferentially used in this context. Regardless of the term used to define it, the microbiome is essential for health and decisive in human diseases.
Translational research: from animal models to treating patients
Animal models are essential in understanding the role of microbiomes in health and diseases whether the endpoint is to improve human or animal health. In basic research and preclinical studies, animal models such as mice, rats, hamsters or others, enable interventions and easy access to organs that would not be possible in humans. The experimental conditions are also more controlled with homogenous genetic backgrounds and by limiting sources of variations (e.g. diet and environmental conditions) affecting microbiota composition.
Despite the great usefulness of animal models, the need for translational research has become critically important in contemporary biomedical research. How to translate findings from basic research and preclinical studies into practical applications and improvements to general public health? Moving from the bench to the bedside requires collaboration among experts from multiple disciplines and also studying different targets. For example, blood sampling is commonly more acceptable for the patient and profiling the circulating microbiome can be as informative as the analysis of biopsies.

Bacterial translocation: the missing link between intestinal microbiome and human complex non-communicable diseases
Complex disorders are multifactorial and often chronic, caused by genetic and environmental factors and comprising hundreds of conditions from cardio-metabolic diseases to neurodegenerative and mental disorders. These pathologies commonly present a low- to high-grade inflammation and have been associated with gut microbiota dysbiosis or a distinct microbial signature. However, how the intestinal microbiome can remotely affect all the parts of the body remains elusive. The translocation of living bacteria and/or bacterial components (e.g. nucleic acids or lipopolysaccharides) from the intestines to the bloodstream and towards other tissues may be the missing link between gut microbiota, systemic inflammation and pathogenesis.
Indeed, bacterial translocation has been shown to play a central role in the onset and/or decompensation of several pathologies, especially in cardio-metabolic disorders and liver diseases. Under pathological conditions, impairment of the intestinal barrier can lead to an increased and/or abnormal bacterial translocation that triggers a cascade of events involving local and systemic inflammation leading to tissue damage and profound metabolic changes.
Atlas of Microbiomes:
What are the levels of bacterial biomass of the different tissues?
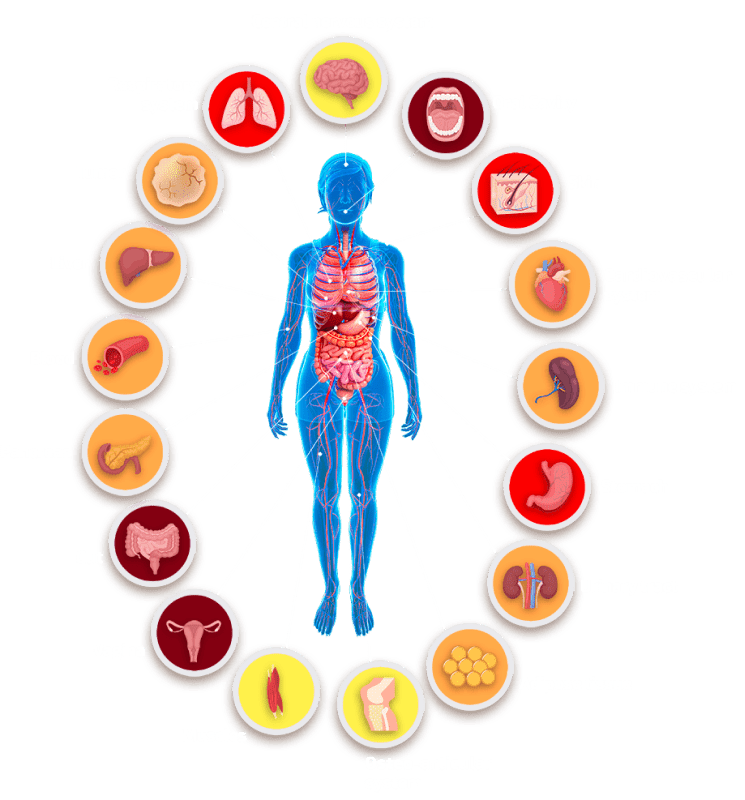
The gut microbiome affects virtually all aspects of human health
Traditional areas of investigation with the microbiome are gastrointestinal diseases (IBD, IBS, CD) and metabolic diseases (obesity and diabetes). In more recent years, new application areas are emerging such as the central nervous system, infectious diseases or cancer. The study of microbiomes beyond the gut is widening the potential for discoveries.

Cardio - metabolic diseases

Liver diseases

Gastrointestinal disorders

Cancer

Neurodegenerative and mental disorders
HIV & infectious diseases

Autoimmune and inflammatory diseases

Nutrition

Kidney diseases

Microbiome in early life
Interrogate the microbial signature in a wide variety of tissues with Vaiomer outstanding expertise
Travel through the fascinating history of microbiome!

Although gut microbiota is by far the most investigated, the concepts of gut and blood microbiomes have grown in parallel since the early stages of the field.
News and views
VAIOMER Experts’ Highlights
Vaiomer will be attending «Journées Polepharma de Microbiomique, 4ème édition»
> Vaiomer will be taking part in the 4th edition of the « Journées Polepharma De Microbiomique » on November 22 & 23 in Rouen, FRANCE.
> Do not miss the amazing “Microbiota and Cancer” session introduced by our CSO, Benjamin LELOUVIER, on Thursday 23 at 14:00.
Vaiomer is taking part to « 7èmes JOURNEES SCIENTIFIQUES FRANCOPHONES du CALM»
>We are excited to exchange and share new ideas with scientists and academics in the field of microbiota and Alzheimer’s research.
>Do not miss our talk presented by Benjamin LELOUVIER in the Microbiota session, on Wednesday, November 15.
Vaiomer is participating in the Genotoul Scientific Day-HOLOBIONTES
> Vaiomer will be attending “Genotoul Scientific Day-HOLOBIONTES: Understanding host microbiota interactions” Thursday, November 9, 2023 in Toulouse, France.

Microbiomes beyond the gut
Learn about the gut, blood and tissue microbiota , the link between gut dysbiosis and tissue inflammation, and discover how these microbiota positively or negatively influence our physiology and can cause disease
More information on the missing link between gut microbiota and circulating microbiomes?

Join Benjamin for a first chat.
Benjamin LELOUVIER
Chief Scientific Officer



